
순열
순열과 조합은 경우의 수 등 가능한 가짓수를 생각할때 가장 바탕이 된다.
우선 순열은 순서가 있는 묶음으로, 7명을 등수를 매기는 방법과 같이 각각 구분되는 형식에 데이터를 나누는 방법이다.
수학적으로 보면 ${}_n\mathrm{P}_{k} = \frac{n!}{(n-k)!}$
7명을 등수를 매기는 방법 $7! = 7\times6\times5\times4\times3\times2\times1 = 5040$
7명 중 1,2,3등을 매기는 방법 $\frac{7!}{(7-3)!} = 7\times6\times5 = 210$ 으로 볼 수 있다.
이러한 순열을 직접 사용하는 경우는 내 생각엔 보통 완전 탐색 등에서 모든 가짓수를 체크하기 위해 사용하는 것 같다.
7명중 1,2,3등을 매길 때 ~ 무슨 조건을 만족하는지 확인하기 위해서, 일단 등수를 다 만들어보는 것이다.
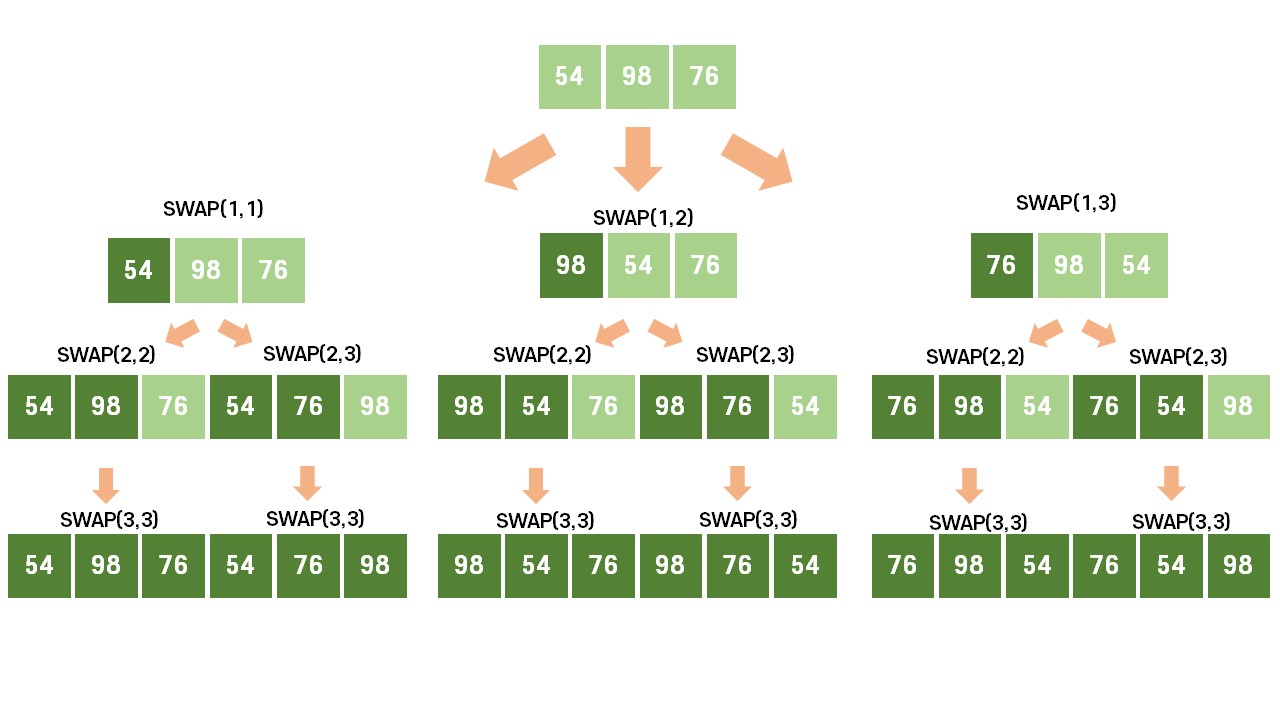
보통 이를 구현하는 방법은 두가지가 있다. 스왑으로 값의 위치를 바꿔가는 방법과, 하나씩 체크하는 방법이 있다.
스왑으로 구현하는 법은 배열의 순서대로 하나씩 바꾸면서 데이터들을 스왑하는 방법이다.
index는 몇 번 까지 묶음이 이루어졌는지 확인하는 수단으로, 이를 기준으로 뒤의 원소들을 바꿔나가는 방법이다.
//JAVA
//nPk (index = 0 부터)
public void PermutationSwap(int[] arr, int index, int n, int k) {
if (index == k) {
for(int i=0;i<k; i++){
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\n");
return;
}
for (int i=index; i<n; i++) {
swap(arr, index, i);
PermutationSwap(arr, index + 1, n, k);
swap(arr, index, i); //다시 원위치
}
}
public void swap(int[] arr, int index, int i) {
int temp = arr[index];
arr[index] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
하나씩 체크하는 방법은, 우리가 머리로 주로 짜는 방법처럼 순열에 사용되지 않은 데이터들을 따로 저장하여 하나씩 대입하는 방법이다. 이 때는 순열의 결과 역시 새로운 배열에 저장해준다.
//JAVA
//nPk (index = 0 부터), newperm에 저장됨
public void PermutationUsed(int[] arr, int index, int n, int k, int[] newperm, int[] used) {
if (index == k) {
for(int i=0;i<k; i++){
System.out.print(newperm[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\n");
return;
}
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
if (used[i] != 1) {
used[i] = 1;
newperm[index] = arr[i];
PermutationUsed(arr, index + 1, n, k, newperm, used);
used[i] = 0; //다시 원래대로
}
}
}
순열은 c++에서 라이브러리로도 사용할 수 있다.
// 첫번째 인자가 구하고자 하는 순열의 시작, 두번째 인자가 순열의 끝
bool next_permutation (BidirectionalIterator first, BidirectionalIterator last);
// 이렇게 사용 가능
do{
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n"
}while(next_permutation(arr.begin(), arr.end());
조합
조합은 순서가 없는 묶음이라고 볼 수 있다. 단순히 그룹을 나누기 때문에 aaab나 baaa나 같은 조합이다.
식으로 표현하면 $_{n}\mathrm{C}_{k}= \frac{{}_n\mathrm{P}_{k}}{!} = \frac{n!}{k!(n-k)!}$
7명 중 3명을 뽑는 방법 $\frac{7!}{3!4!} = 7\times6\times5\div3\div2\div1 = 35$
조합도 순열과 비슷하게 직접 조합들을 짜서 사용해야 될 때가 있다.
조합의 구현에서 가장 핵심인 식은 파스칼의 삼각형에서도 나온 $_{n}\mathrm{C}_{k} = _{n-1}\mathrm{C}_{k-1} + _{n-1}\mathrm{C}_{k} $ 이다.
하나의 원소를 선택한 경우 $_{n-1}\mathrm{C}_{k-1}$와, 선택 안한 경우 $_{n-1}\mathrm{C}_{k}$로 계속해서 나아가면 된다.
//JAVA
//nCk (index = 0 부터 k개, t는 남은 데이터)
public void Combination(int[] arr, int index, int n, int k, int t, int[] newcomb) {
if(k == 0) {
for(int i=0; i<newcomb.length; i++){
System.out.print(newcomb[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\n");
return;
}
if(t == n) return;
newcomb[index] = arr[t];
Combination(arr,index+1, n, k-1,t+1, newcomb); //선택했을 때
Combination(arr,index, n, k, t+1, newcomb); //선택 안했을 때
}
만약 여기서 중복조합 (같은것도 가능하게)로 하고 싶다면 아래와 같이 바꿔주면 된다.
newcomb[index] = arr[t];
//Combination(arr,index+1, n, k-1,t+1, newcomb); //선택했을 때
Combination(arr,index+1, n, k-1,t, newcomb); //남은 데이터 t를 늘리지 않음
Combination(arr,index, n, k, t+1, newcomb); //선택 안했을 때
'알고리즘 > 스터디' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 12. 그래프 (2) (최단경로, 프림, 크루스칼) (0) | 2020.09.14 |
|---|---|
| 11. 그래프 (1) (인접행렬, 인접리스트, DFS, BFS) (0) | 2020.09.10 |
| 9. 최대, 최소 찾기 (순차, 토너먼트, 선택 알고리즘) (0) | 2020.09.01 |
| 8. 탐색 - 선형 탐색, 이진 탐색, 이진 탐색 트리, 해시 탐색 (0) | 2020.08.25 |
| 7. 정렬 (2) - 합병 정렬, 힙 정렬, 쉘 정렬 (0) | 2020.08.18 |

Comment